In the dynamic landscape of digital transactions, it’s crucial for businesses, especially Software as a Service (SaaS) companies, to stay abreast of various payment methods and their associated processes. One payment method that holds significant importance is Automated Clearing House (ACH) transactions.
Understanding what ACH is, how ACH works, as well as subsequent processes like ACH returns is fundamental for SaaS businesses to efficiently manage their finances and maintain customer satisfaction.
What is ACH?
ACH (Automated Clearing House) is a network in the United States for electronic payments and transfers between bank accounts, facilitating transactions such as consumer transactions, direct deposits, and bill payments. It offers a more efficient and cost-effective alternative to traditional paper-based methods like checks.
How does ACH Work?
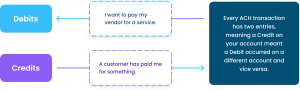
The ACH rail supports pushing and pulling funds from a US Bank Account. This means it can be used for purchases, payroll, and pretty much any use case as long as you have an originating and receiving bank account on either side of the request. See the diagram below.
What is an ACH Return?
An ACH return is a process where an ACH transaction is sent back to the originating bank by the receiving bank. There are several reasons why an ACH transaction may be returned, including insufficient funds, invalid account numbers, incorrect information, or issues with the account holder’s authorization. When a transaction is returned, the funds are not transferred and the payment is considered unsuccessful. It is important for businesses to understand with ACH returns that just because you set up a payment, doesn’t mean it is completed.
- What is the Flow of the ACH Return Once It Has Been Initiated? (AKA how do ACH returns happen?)

- Once initiated and depending on the return code, a return can take 2 banking days to up to 60 calendar days to process.
Why ACH Returns Matter for SaaS Businesses?
With ACH returns, the RDFI is responsible for initiating the return entry or the return for the total amount of the original payment (partial returns are not permitted).
ACH returns not only incur fees and lose revenue for merchants but also endanger a merchant’s ability to use ACH payments. If a merchant incurs too many ACH returns, their ability to use the ACH network can be revoked altogether.
There are other implications around ACH Returns for SaaS businesses, including:
Cash Flow Management: ACH returns can disrupt cash flow for SaaS businesses, especially those operating on subscription-based models. Failed payments mean delayed revenue, which can impact budgeting, forecasting, and overall financial stability.
Customer Experience: Payment failures can result in customer dissatisfaction and churn. For SaaS businesses, where customer retention is paramount, failed transactions due to ACH returns can damage relationships and erode trust. Customers expect seamless payment experiences, and frequent returns can tarnish a company’s reputation.
Compliance and Risk Mitigation: Understanding ACH regulations and compliance requirements is crucial for SaaS businesses to mitigate risk and avoid potential penalties. Non-compliance with ACH rules can lead to fines and legal consequences. By proactively managing ACH returns and adhering to industry standards, businesses can reduce compliance risks.
Operational Efficiency: A high volume of ACH returns can strain operational resources as businesses need to investigate and resolve payment issues promptly. Implementing efficient processes and leveraging the right payment solutions for ACH management can streamline operations and reduce the administrative burden associated with returns.
How Can SaaS Businesses Address ACH Returns?
Partnering with the Right Payment Provider: Utilize a payment provider that offers robust ACH processing capabilities and built-in features for managing returns. These platforms often provide monitoring, reporting, and automated retry mechanisms to help minimize returns.
Data Verification and Validation: Implement account verification processes to ensure the accuracy of customer information before initiating ACH transactions. Validating account details can reduce the likelihood of returns due to incorrect or incomplete data.
Communication and Notification: Maintain transparent communication with customers regarding payment failures and ACH returns. Promptly notify customers of any issues and provide clear instructions for resolving payment discrepancies to mitigate dissatisfaction and preserve relationships.
Risk Assessment and Fraud Prevention: Implement risk assessment protocols to identify and mitigate potential fraud risks associated with ACH transactions. Utilize fraud detection tools and monitoring systems to detect suspicious activity and prevent unauthorized transactions.
In conclusion, ACH transactions and ACH returns play a significant role in the payment ecosystem, particularly for SaaS businesses reliant on recurring revenue streams. By understanding the fundamentals of ACH, actively managing returns, and implementing best practices for ACH processing for PayIn, SaaS companies can enhance cash flow, preserve customer relationships, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, ultimately driving long-term success in the digital economy. There are other implications as it relates to ACH for PayOut, which we will cover in more detail in a future blog post.
Looking to learn more about how Payabli helps SaaS companies like yours better handle ACH and ACH Returns? Schedule some time to speak with one of our Payment Experts.
